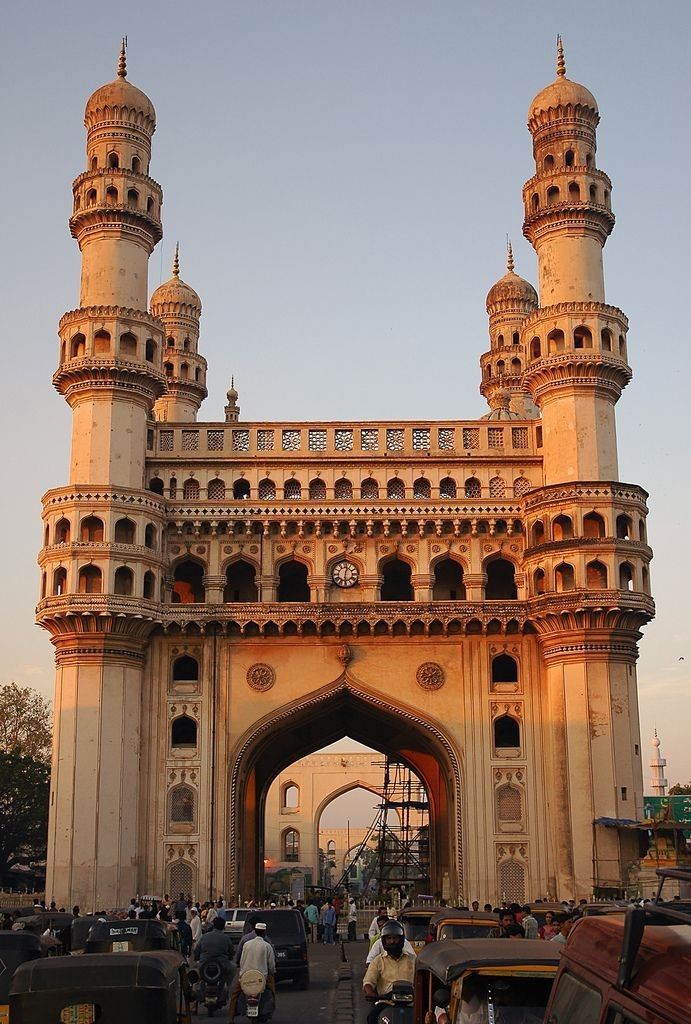
THE BEST HISTORICAL MONUMENTS OF INDIAN
India’s monuments showcase rich heritage, architecture, and cultural significance worldwide.
India's Timeless Monuments

Percy Brown (Architectural Historian)
Artistic, Grand, Symmetrical, Spiritual, Timeless.
Percy Brown admired Indian architecture for its artistic brilliance and structural ingenuity, highlighting Hindu temples like Khajuraho and Brihadeeswarar as “monuments of unparalleled craftsmanship,” blending spirituality with intricate carvings, towering vimanas, and timeless grandeur.
He praised Mughal architecture for its elegance, symmetry, and fusion of Persian and Indian influences. Calling the Taj Mahal “the most exquisite monument ever built,” he also admired Fatehpur Sikri’s planning and Indo-Islamic innovation.
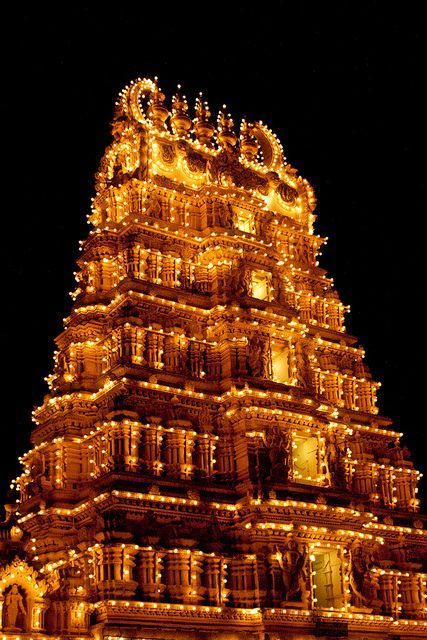
Timeless Grand Heritage
Majestic, Intricate, Spiritual, Iconic.
Indian architecture blends tradition, innovation, and spirituality. From Khajuraho’s intricate carvings to the Taj Mahal’s grandeur, it showcases artistic mastery. Temples, forts, and stepwells reflect cultural evolution, merging indigenous and foreign influences into a timeless legacy.
Services
Reprocessing
Narrative Therapy
Quisque aliquet velit sit amet sem interdum faucibus. In feugiat aliquet mollis etiam tincidunt ligula.
Trauma Therapy
Luctus lectus non quisque turpis bibendum posuere. Morbi tortor nibh, fringilla sed pretium sit amet.
Reprocessing
Narrative Therapy
Trauma Therapy

